Windows Update Standalone Installer commonly known as WUSA (wusa.exe) was introduced in Windows Vista. Since then its part of Windows family and is still available in latest builds of Windows 10. Inside this post, we’ll learn about Windows Update Standalone Installer in Windows 10, in detail.
Page Contents
Windows Update Standalone Installer in Windows 10
WUSA is basically an installation agent used to install Windows Updates from update package files with .msu extension. Windows by default, set the .msu extension to get handled with WUSA. wusa.exe sits in System32 folder of system root drive.
Here, not to be confused between .cab file and .msu files. As I mentioned, .msu files are update packages and WUSA handles them nicely, whereas .cab files are often archived or compressed cabinet files that contains drivers update and other Windows components update. They’re not alone handled by WUSA, but with other installation engines as well, such as Windows Installer etc. A .msu file may contain several .cab files in it, where each .cab file representing an update. A .cab file may not be installed with WUSA, here’s the guide to install updates on .cab files.
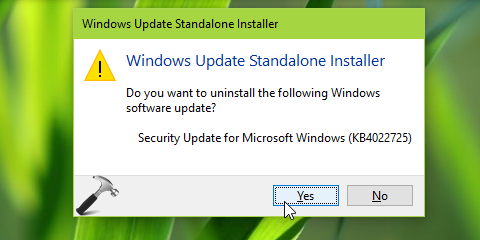
WUSA is responsible to verify, install and uninstall Windows Updates in Windows OS. At a time, WUSA can install single update in a separately held session. Hence when you install an update, make sure you complete its installation before you go ahead for another update. WUSA doesn’t allows you to:
1. Uninstall an update, that is mandatory for your system.
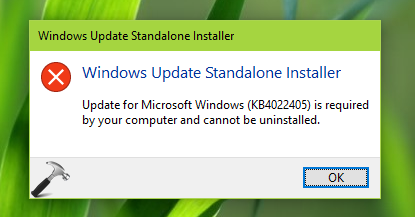
2. Install an update, which is not applicable to your computer.
WUSA Command Line Switches in Windows
The general syntax to use WUSA are as follows. Here, items mentioned in bold green color are general switches and they can be used per condition.
For installing updates via MSU file:
For uninstalling MSU file:
For uninstalling updates via Knowledge Base (KB) number/ID:
wusa </?, /h, /help> can be used to view help for Windows Update Standalone Installer.
The usage of general switches is mentioned below:
| Switch | Usage |
|---|---|
| /quiet | Run WUSA in quiet mode without user interaction. When the tool runs in quiet mode, it runs without user interaction. The computer restarts if this is required.
For example, |
| /norestart | Prevents WUSA from restarting the computer. The /norestart switch is ignored if the /quiet switch is not present. If you run WUSA together with these two switches, you must manually restart the operating system after the installation is complete if the installation requires you to restart the computer.
For example, |
| /warnrestart | When this switch is combined with the /quiet switch, WUSA prompts you before it begins a restart for install and uninstall operations.
For example, |
| /forcerestart | When this switch is combined with the /quiet switch, WUSA forcibly closes applications and then begins a restart.
For example, |
| /logfile | WUSA writes the log file with installer with this switch. |
| /uninstall | Uninstalls the specified package or KB number.
For example, Read more about how to uninstall updates in Windows 10. |
| /kb | Specifies the package to be uninstalled by using its KB number. Can be passed only together with the /uninstall switch.
For example, |
So this is all about WUSA. Hope you find the article useful!
![KapilArya.com is a Windows troubleshooting & how to tutorials blog from Kapil Arya [Microsoft MVP (Windows IT Pro)]. KapilArya.com](https://images.kapilarya.com/Logo1.svg)









Leave a Reply