In Windows, there are many useful command-line tools which can help you manage the OS quickly. By command-line tool, we mean the command with supported parameters. One of those useful command-line tool is chkdsk.
chkdsk is the short form or command utilized for checking and fixing disk/file errors. Though Windows provides you options via user interface to perform disk error checking, however chkdsk has its own importance. It can work in pre-boot environment and help user to fix disk problems instantly. Microsoft says, “chkdsk checks the file system and file system metadata of a volume for logical and physical errors”.
Using chkdsk Command Line Tool In Windows
chkdsk command-line tool can be used in following cases:
- If a disk on your system is slow and freezing
- To check and fix faulty or bad sectors on disk
- To check and fix disk corruption
- To check and fix file system errors
Following is the syntax for general chkdsk command-line tool:
chkdsk [{Volume}[[{Path}]{FileName}]] [/f] [/r] [/x] [/l[:{Size}]]
Usage of important parameters mentioned below:
| Paramater for | Parameter | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Specify disk to check | {Volume}
{Path} {FileName} |
Use {Volume} to specify disk volume, {Path} to specify FAT32 file, {FileName} to specify FAT32 file. Note that {Path} and {FileName} not applicable to NTFS file system.
For example, |
| Fix error | /f | Use /f parameter to fix disk/file errors. For example, chkdsk C: /f will check C: drive and fix errors. |
| Recovery | /r | Use /r to recover information housing on disk’s faulty sectors. For instance, chkdsk C: /r will recover information on C: drive bad sectors. |
| Dismount volume | /x | Use /x to force Windows to dismount disk volume first, if required. If you’ve using /x, you don’t need to additionally use /f parameter as /x already contains functions of /f. For example, chkdsk C: /x will dismount volume, check disk and fix errors on C: drive. |
| Log size | /l[:{Size}] | Use /l parameter to display current chkdsk log file size. Use :{Size} parameter to specify the log file size. |
To use chkdsk command-line tool, perform these steps:
1. Open Command Prompt as administrator.
2. In the Command Prompt window, type the chkdsk command by substituting required parameters.
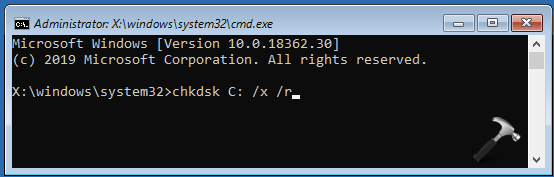
3. Press Enter key to execute the command. You’ll see the scan results as shown in below screenshot.
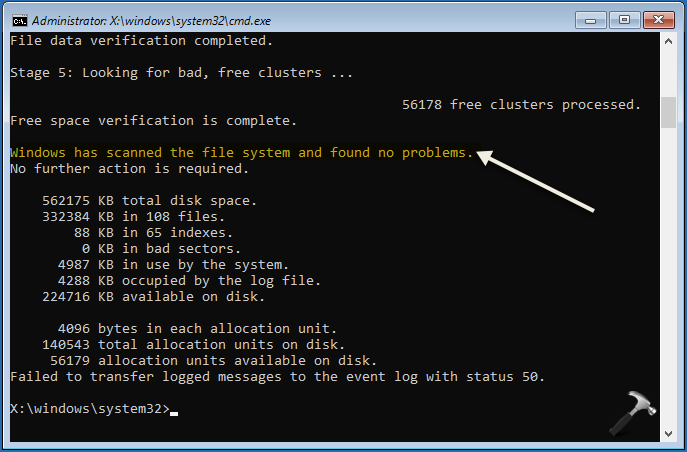
4. Close Command Prompt, once execution completes.
Interested users may check this Microsoft’s documentation for additional information on chkdsk tool.
Hope you find the post useful!
Also see: Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process.
![KapilArya.com is a Windows troubleshooting & how to tutorials blog from Kapil Arya [Microsoft MVP (Windows IT Pro)]. KapilArya.com](https://images.kapilarya.com/Logo1.svg)










Leave a Reply