As an IT administrator, you can provide updates to your clients via local server/service. We’ve previously shared you following article regarding this:
How To Specify Intranet Update Service Location In Windows 10
When you allow Windows to have updates from your local source, these updates must be signed by Microsoft. In other words, to maintain security of your system, Windows will not allow those updates that are not signed by Microsoft. This is the default and expected behaviour. However, if you like, you can tell Windows to allow signed updates from your local update source. Still, the necessary condition is that your local source updates must be signed from Trusted Publisher.
In this article, we’ll see how you can allow signed updates from a Trusted Publisher with your local update source.
Allow Signed Updates From An Intranet Microsoft Update Service Location
Windows doesn’t provides a native UI settings for this. But as usual, you can go ahead and configure a dedicated Group Policy setting to avail this benefit. We’ve described below process for a Windows Server. Equivalent steps can be taken by Windows 10 clients.
1. Open Group Policy Management window by running gpmc.msc command.
2. In the window, you can create a relevant GPO object or link it to an existing one. Right click on GPO object and created so far and select Edit.
3. Under GP Editor, go to following location:
Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Update

4. Look for Allow signed updates from an intranet Microsoft update service location policy setting and double click on it. Set it to Enabled status and click Apply, OK.
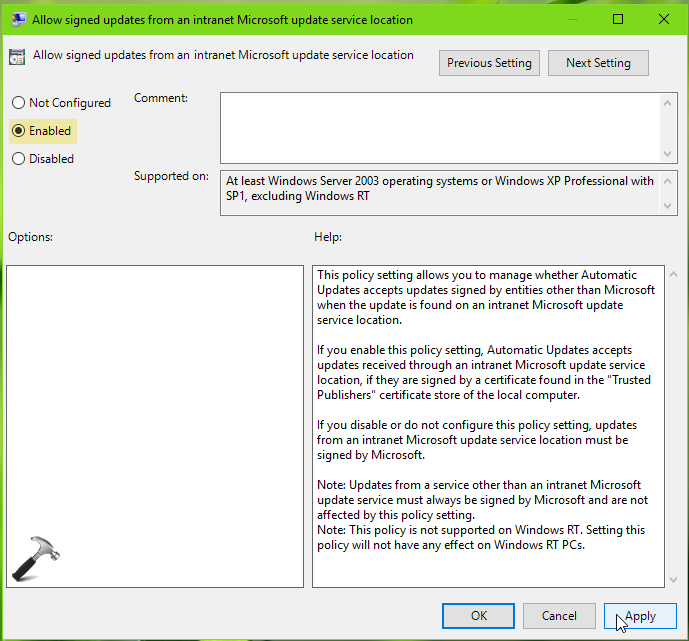
5. Exit Group Policy Management and update GP engine by running gpupdate /force command.
Once the GP engine updated, you can push signed updates to your clients from a Trusted Publisher via local source.
That’s it!
![KapilArya.com is a Windows troubleshooting & how to tutorials blog from Kapil Arya [Microsoft MVP (Windows IT Pro)]. KapilArya.com](https://images.kapilarya.com/Logo1.svg)


![[Latest Windows 10 Update] What’s new in KB5055612? [Latest Windows 10 Update] What’s new in KB5055612?](https://www.kapilarya.com/assets/Windows10-Update.png)






Leave a Reply